According to Newtons 1st Law the soccer ball will move if Marissa applies an unbalanced force. According to Newtons 2nd Law a soccer ball will accelerate more than a basketball because the soccer ball has less mass.

Soccer Physics Of Soccer Newton S Laws Of Motion Physics Newtons Laws Of Motion Newtons Laws
Use newtons law of motion to describe what happens when you kick a soccer ball.
. Up to 24 cash back If the man with the ball is the motion and the defensive player is the unbalanced force it acts upon the first law. Yoel Rodríguez Writing Fellow. Regarding kickball before the ball is kicked by the pitcher the ball is on the ground at rest.
A soccer player kicks a soccer ball. When using this set just type the number of the law it is making reference to. A soccer ball is sitting at rest.
If the two soccer players were to collide with each other both of them would experience forces that are opposite in. Once you kick the ball you exert force onto it that makes the ball accelerate from the force and mass. Newtons Third Law of Motion is defined as For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
Just kicking the soccer ball relates to the physics of motion the physic of friction and even aerodynamics. This balanced force results in no change of motion. When its flying in the air the ball is motionless because of inertia until it is kicked again.
The soccer ball when kicked keeps going forward until friction a person or another object like a wall stops it. 04 kg 2500 ms 2 1000 theref ore the player would need to exert 1000 Newtons of force on the soccer ball in order to accelerate it the desired amount. The tendency of an object to resist changes in its state of motion The First Law states that all objects have inertia.
Newtons Third Law declares. Kicking a soccer ball is not a newtons first law because newtons first law says thatEvery body continues in its state of rest or of uniform motion in a. The ball exerts an equal force back on the soccer players foot.
An object at rest tends to stay at rest and an object in motion tends to stay in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Newtons Second Law. Describe two instances when Jenny is kicking the ball that are examples of equal and opposite forces.
If I kick my soccer ball harder than my friend it will go farther and be quicker. Define how each of Newtons Laws applies to Marissa kicking a soccer ball or a car moving away from a stop light. For every external force there is an equal force acting in the opposite direction.
In order to deal successfully with physical situations involving the interlocking physical notions of force friction acceleration and velocity students must be able to create and free-body diagrams that accurately represent. Newtons First Law is also called the Law of Inertia Inertia. Newtons 3 Laws of Motion Which law.
Newtons third law of motion can be used to discuss equal and opposite reaction forces. Newtons second law of. Newtons first law states that because the ball is at a rest it will stay that way until the ball is acted upn by an unbalanced force.
SECOND LAW 2 Fma. When a soccer ball is resting non moving on the ground it will stay like that until someone kicks it or another force acts upon it. These are especially good science project ideas for kids who like to move.
Newtons First Law. To first order the center of gravity for a soccer ball is located at the exact center of the ball. Newtons second law of motion When a kicker kicks the ball he has to use a great amount of force.
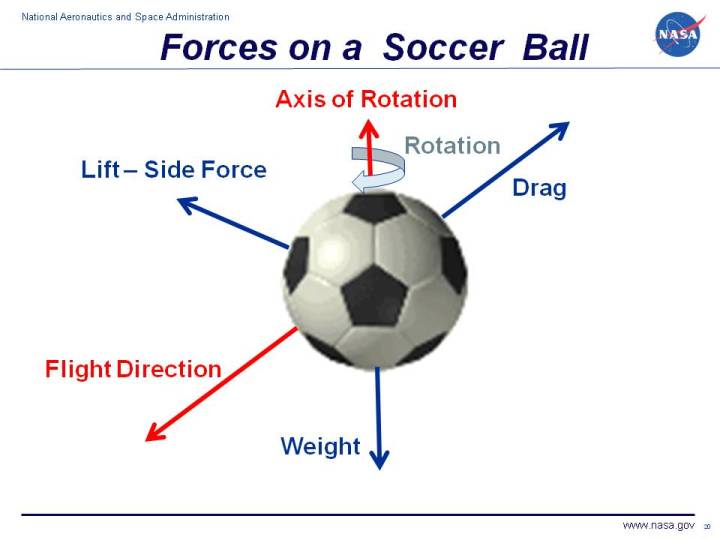
Drag As the ball moves through the air the air resists the motion of the ball and the resistance force is called drag. If we want to use one word to describe this law it is Karma. Newtons laws of motion describe the translation of the center of gravity.
Imagine a scenario where two opposing players are physically pushing or shouldering each other in order to get the ball. You have to get the angles right and the acceleration. Newtons Laws of Motion Informal Assignment Instructor.
Soccer Physics of Soccer Newtons Laws of Motion. You get back as much as you give and apparently it is a physical law and not just a philosophical concept. They are great concepts to explore by doing a science experiment.
How Newtons Laws of Motion Apply to Soccer 2nd Law of Motion Example 1 1st Law of Motion Newtons first law states that an object at rest will stay at rest an object in motion will stay in motion unless acted on by an unbalanced force In soccer a ball resting in the grass. Newtons 1st Law of Motion - As called Law of inertia the object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays at motion with the same speed and same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. In flight the ball rotates about the center of gravity.
Newtons Laws of Motion in Soccer. For Newtons Laws Of Motion. It states that any object at rest will tend to stay at rest and any object in motion will tend to stay in motion unless acted on by an unbalanced force.
But that is not the only thing. Up to 24 cash back law 1 in soccer. Describe-Use Newtons laws of motion to describe what happens when you kick a soccer ball.
Newtons first law plays a role in soccer. When you first kick the soccer ball you would have exerted a force on it that would make it accelerate due to the force and the mass and then while it is in the air the soccer ball will become an example of inertia and then finally the ball will rest until an unbalanced force acts on the soccer ball. Newtons Laws of Motion explain force and motion or why things move the way they do.
It is known that the object at rest stays at rest. In soccer this means that when the ball is kicked to the direction of where you want it to go and you have added the amount of force that you wanted to add to the ball it does the same back to your foot. The first law of motion is called the Law of Inertia.
The acceleration of the ball depends upon how much force behind the kick. Newtons Third Law of Motion states that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. Use Newtons first law of motion.
The first law is perhaps the most readily observable on the soccer field. According to Newtons Second Law the force behind the soccer ball equals its mass times acceleration in the equation F ma. A hard kick will move the soccer ball farther and faster than a soft kick.
The concepts can often be explained using sports equipment or by understanding how amusement park rides work. Newtons Third Law. It takes an unbalanced force of a kick to change its motion.
V final velocity a acceleration t time.

0 Comments